Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a condition that affects blood flow to the limbs due to narrowed or blocked arteries. In this blog post, we will see the various methods used to diagnose PAD effectively.
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a type of peripheral vascular disease characterized by the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels outside the heart, particularly affecting the legs and feet. This condition can lead to reduced blood flow, causing symptoms like leg pain and non-healing wounds.
Causes of Peripheral Arterial Disease
The primary cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits build up in the arteries, reducing blood flow. Other causes include inflammation, injury, radiation exposure, and infections. Individuals with coronary artery disease are at higher risk of developing PAD.
Symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease
The symptoms of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) include:
- Pain in the legs when walking (intermittent claudication), which usually disappears after resting.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs.
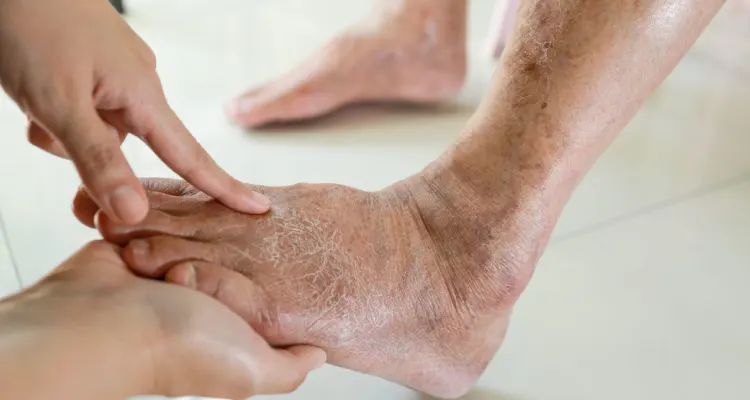
- Ulcers (open sores) on the feet and legs that do not heal.
- Changes in skin color on the legs, such as turning paler than usual or blue.
- Muscle wasting in the legs.
- Severe burning pain in the legs and feet that continues even at rest (critical limb ischemia).
- Skin turning pale, shiny, smooth, and dry.
- Wounds and ulcers on the feet and legs that do not heal.
- Loss of muscle mass in the legs.
- The skin on the toes or lower limbs becomes cold, numb, red, black, and swollen, and produces smelly pus (gangrene).
These symptoms can vary in severity and may indicate different stages of PAD, from intermittent claudication to critical limb ischemia, which is a severe complication that requires immediate medical attention.
How is Peripheral Arterial Disease Diagnosed?
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors evaluate symptoms, and risk factors, and perform a physical exam looking for signs like weak pulses and poor wound healing.
2. Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
The ankle-brachial index (ABI) test is a noninvasive procedure used to diagnose Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) by comparing blood pressure in the ankles to that in the upper arms. This test helps identify narrowed or blocked arteries in the legs, which can reduce blood flow to the limbs, leading to symptoms like leg pain while walking and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
3. Doppler Ultrasound
Using sound waves, Doppler ultrasound evaluates blood flow in arteries to detect blockages or narrowing indicative of PVD.
4. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
MRA uses magnetic fields to create detailed images of blood vessels, helping visualize blood flow abnormalities in PAD.
5. Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
CTA provides detailed images using X-rays and contrast dye to identify blockages accurately in the legs, making it a reliable diagnostic tool for PAD.
6. Angiography
Considered the gold standard for PAD diagnosis, angiography involves injecting contrast dye into arteries to visualize blockages or narrowing in real time using X-ray imaging.
Complications of Untreated Peripheral Arterial Disease
Untreated PAD can lead to severe complications like non-healing wounds, tissue damage, gangrene, critical limb ischemia, heart attack, and stroke. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to prevent these outcomes.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection of PAD is crucial for preventing progression to advanced stages that may require invasive interventions like amputation. Lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring can help manage PAD effectively.
Understanding how Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is diagnosed is essential for timely management and prevention of complications. If you experience symptoms suggestive of PAD, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. Remember, early detection saves limbs and lives!
For more information on the Diagnosis of Peripheral Artery Disease, consult Dr. Kunal Arora or Contact us at +91 90040 93090.